Discover peace of mind through proactive healthcare with Align Radiology’s Preventive Screening Services in Laurel. At Align Radiology, we specialize in advanced imaging techniques that detect potential health issues early, allowing for timely intervention and personalized care. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert staff ensure accurate results and a comfortable experience, empowering you to take control of your health. Schedule your preventative screening today and align yourself with a healthier tomorrow at Align Radiology.
Preventive Screening
Preventive Screening
Preventive Screening
Discover peace of mind through proactive healthcare with Align Radiology’s preventative screening services. At Align Radiology, we specialize in advanced imaging techniques that detect potential health issues early, allowing for timely intervention and personalized care. Our state-of-the-art facilities and expert staff ensure accurate results and a comfortable experience, empowering you to take control of your health. Schedule your preventative screening today and align yourself with a healthier tomorrow at Align Radiology.
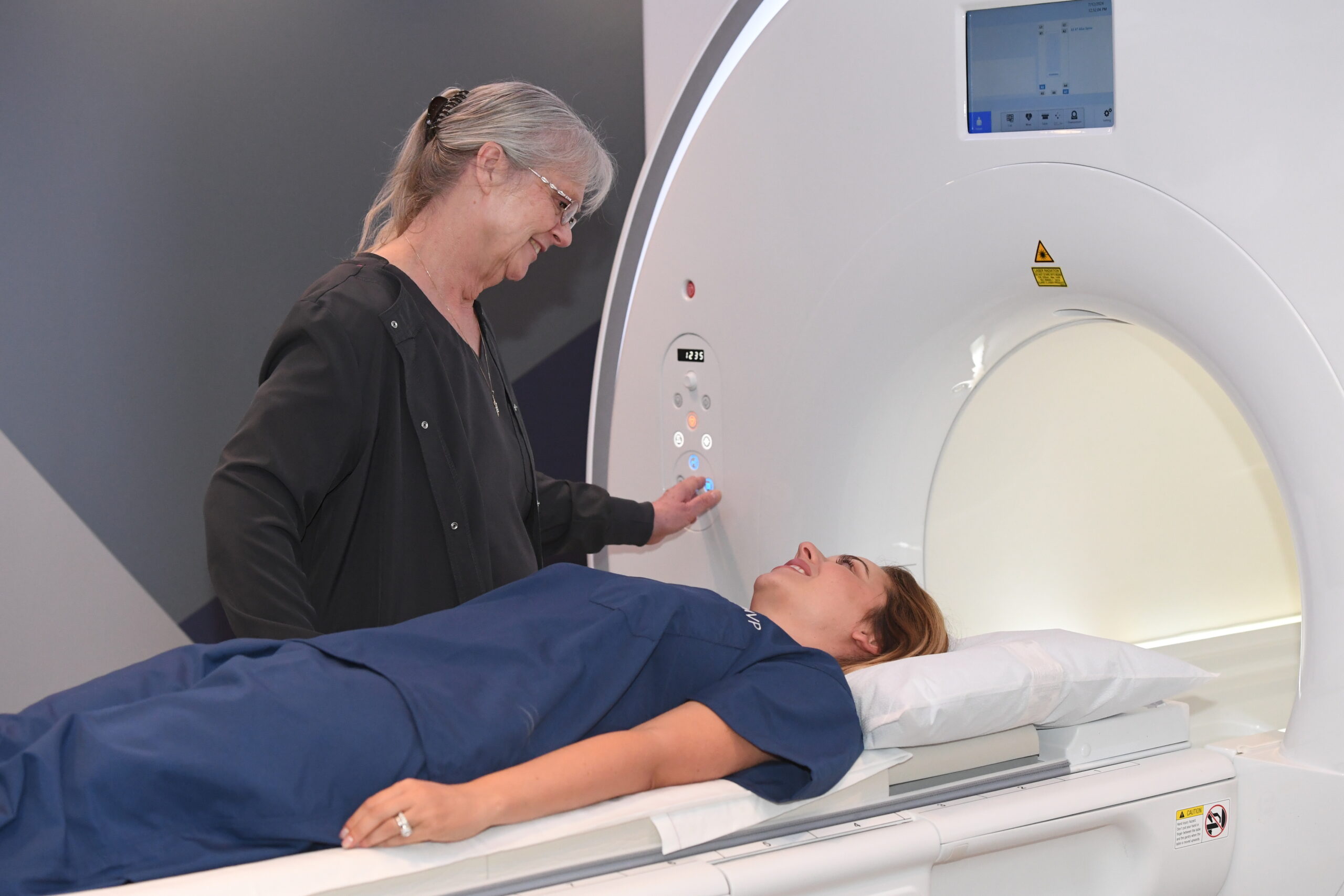
Full body MRI
Full body MRI imaging represents a cutting-edge advancement in medical diagnostics, offering a holistic view of a patient’s health in a single scan. This comprehensive imaging technique excels in detecting a wide range of conditions, from tumors and vascular abnormalities to musculoskeletal injuries, without the use of ionizing radiation. By providing detailed insights into the body’s internal structures, organs, and soft tissues, it enables early detection and accurate diagnosis of diseases, facilitating timely interventions and personalized treatment plans. Book your Preventive Screening Services in Laurel now.

Full body MRI
Full body MRI imaging represents a cutting-edge advancement in medical diagnostics, offering a holistic view of a patient’s health in a single scan. This comprehensive imaging technique excels in detecting a wide range of conditions, from tumors and vascular abnormalities to musculoskeletal injuries, without the use of ionizing radiation. By providing detailed insights into the body’s internal structures, organs, and soft tissues, it enables early detection and accurate diagnosis of diseases, facilitating timely interventions and personalized treatment plans.
Lung Cancer Screening
Our low-dose lung cancer screening program, utilizing advanced low-dose CT technology, offers a quick and non-invasive way to detect lung cancer early. Ideal for individuals aged 50-80 with a heavy smoking history, this screening can identify lung cancer before symptoms arise, significantly increasing treatment success. Consult with our healthcare professionals to see if you’re eligible and take a vital step towards protecting your health. Early detection is key – schedule your screening today.
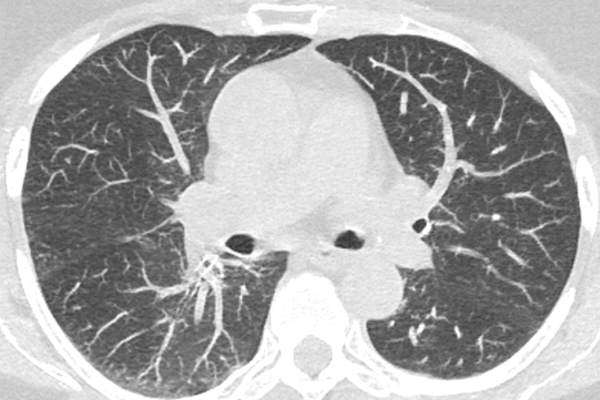
Lung Cancer Screening
Our low-dose lung cancer screening program, utilizing advanced low-dose CT technology, offers a quick and non-invasive way to detect lung cancer early. Ideal for individuals aged 50-80 with a heavy smoking history, this screening can identify lung cancer before symptoms arise, significantly increasing treatment success. Consult with our healthcare professionals to see if you’re eligible and take a vital step towards protecting your health. Early detection is key – schedule your screening today.

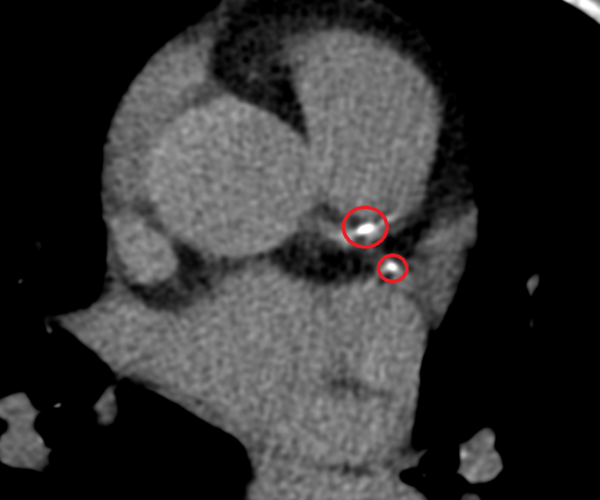
Cardiac Screening
A calcium score CT, also known as a coronary calcium scan, is a specialized type of computed tomography (CT) scan that is designed to detect the presence of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. This plaque, which is composed of calcium, fats, and other substances, can harden over time and potentially narrow or block the coronary arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease or a heart attack.
The calcium score CT scan is non-invasive and quick, usually taking only a few minutes. During the procedure, the patient lies on a table inside a CT scanner. The machine takes several detailed images of the heart and the coronary arteries. These images are then analyzed to detect the presence and extent of calcified plaque. The amount of plaque is quantified as a “calcium score.” A higher calcium score indicates a greater amount of calcified plaque and a higher risk of coronary artery disease.
The results of the scan can help healthcare providers assess a patient’s risk for heart disease and guide decisions about lifestyle changes or medications to reduce this risk. This scan is particularly useful for people who have intermediate risk factors for heart disease, such as a family history of heart disease, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, or smoking.
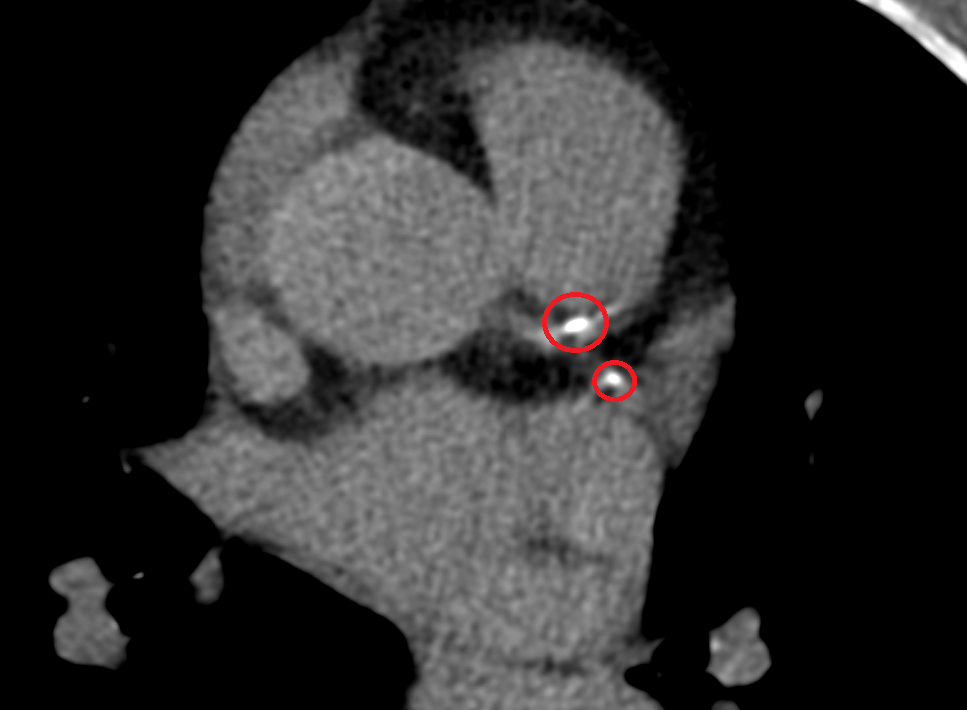
Cardiac Screening
A calcium score CT, also known as a coronary calcium scan, is a specialized type of computed tomography (CT) scan that is designed to detect the presence of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. This plaque, which is composed of calcium, fats, and other substances, can harden over time and potentially narrow or block the coronary arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease or a heart attack.
The calcium score CT scan is non-invasive and quick, usually taking only a few minutes. During the procedure, the patient lies on a table inside a CT scanner. The machine takes several detailed images of the heart and the coronary arteries. These images are then analyzed to detect the presence and extent of calcified plaque. The amount of plaque is quantified as a “calcium score.” A higher calcium score indicates a greater amount of calcified plaque and a higher risk of coronary artery disease.
The results of the scan can help healthcare providers assess a patient’s risk for heart disease and guide decisions about lifestyle changes or medications to reduce this risk. This scan is particularly useful for people who have intermediate risk factors for heart disease, such as a family history of heart disease, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, or smoking.

